UCLA: Statistical Consulting Groupのページから。
UCLAではMplusのコードが書かれているが、このエントリでは、同じ分析をRのlavaanでの再現したいと思う。
Mplus
パス解析はすべての変数が観測される方程式系を推定するために使用される。潜在変数を含むモデルとは異なり、パス・モデルは,観察された変数の完全な測定を仮定する。観察された変数間の構造的関係のみがモデル化される。このタイプのモデルは、1つまたは複数の変数が他の2つの変数の関係を媒介すると考えられる場合によく使用されます(媒介モデル)。同様のモデル設定は、2つの無関係な従属変数の誤差(残差)が相関することが許されるモデル(一見無関連回帰)や、変数間の関係がグループ間で異なると考えられるモデル(多重グループモデル)の推定に使用することができる。
1.特定モデル
このページの例では、回答者の高校時代の成績 (hs), 大学時代の成績 (col), GRE のスコア (gre), そして大学院時代の成績 (grad) という 4 つの変数を含むデータセット (https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/path.dat) を使用している。GREスコアは高校と大学のGPA(それぞれhsとcol)を使って予測し、大学院のGPA(grad)はGRE、高校GPA、大学GPAを使って予測します。このモデルは、ちょうど同定され、自由度がゼロであることを意味する。
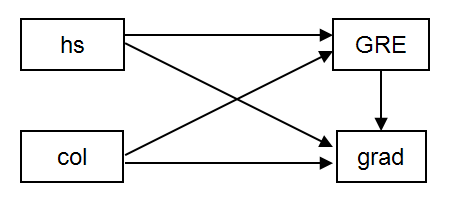
model: コマンドでは、on というキーワードで gre を hs と col に、grad を hs、col、gre に回帰させることを表しています。output: コマンドに stdyx; オプションをつけると、標準化された回帰係数とR2乗の値が得られる(stdyx; オプションは、回帰係数とR2乗の値が得られます)。(stdyx;オプションはyとxの両方で標準化された係数を生成するが、他のタイプの標準化も可能で、standardized;オプションを使って要求できる)。
Title: Path analysis -- just identified model
Data:
file is https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/path.dat ;
Variable:
Names are hs gre col grad;
Model:
gre on hs col;
grad on hs col gre;
Output:
stdyx;
以下は、Mplusからの出力である。
INPUT READING TERMINATED NORMALLY
Path analysis -- just identified model
SUMMARY OF ANALYSIS
Number of groups 1
Number of observations 200
Number of dependent variables 2
Number of independent variables 2
Number of continuous latent variables 0
Observed dependent variables
Continuous
GRE GRAD
Observed independent variables
HS COL
Estimator ML
Information matrix OBSERVED
Maximum number of iterations 1000
Convergence criterion 0.500D-04
Maximum number of steepest descent iterations 20
Input data file(s)
https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/path.dat
Input data format FREE
THE MODEL ESTIMATION TERMINATED NORMALLY
TESTS OF MODEL FIT
Chi-Square Test of Model Fit
Value 0.000
Degrees of Freedom 0
P-Value 0.0000
Chi-Square Test of Model Fit for the Baseline Model
Value 247.004
Degrees of Freedom 5
P-Value 0.0000
CFI/TLI
CFI 1.000
TLI 1.000
Loglikelihood
H0 Value -2789.415
H1 Value -2789.415
Information Criteria
Number of Free Parameters 9
Akaike (AIC) 5596.830
Bayesian (BIC) 5626.515
Sample-Size Adjusted BIC 5598.002
(n* = (n + 2) / 24)
RMSEA (Root Mean Square Error Of Approximation)
Estimate 0.000
90 Percent C.I. 0.000 0.000
Probability RMSEA <= .05 0.000
SRMR (Standardized Root Mean Square Residual)
Value 0.000
MODEL RESULTS
Two-Tailed
Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value
GRE ON
HS 0.309 0.065 4.756 0.000
COL 0.400 0.071 5.625 0.000
GRAD ON
HS 0.372 0.075 4.937 0.000
COL 0.123 0.084 1.465 0.143
GRE 0.369 0.078 4.754 0.000
Intercepts
GRE 15.534 2.995 5.186 0.000
GRAD 6.971 3.506 1.989 0.047
Residual Variances
GRE 49.694 4.969 10.000 0.000
GRAD 59.998 6.000 10.000 0.000
STANDARDIZED MODEL RESULTS
STDYX Standardization
Two-Tailed
Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value
GRE ON
HS 0.335 0.068 4.887 0.000
COL 0.396 0.068 5.859 0.000
GRAD ON
HS 0.356 0.070 5.073 0.000
COL 0.108 0.073 1.467 0.142
GRE 0.326 0.067 4.869 0.000
Intercepts
GRE 1.643 0.378 4.343 0.000
GRAD 0.651 0.350 1.859 0.063
Residual Variances
GRE 0.556 0.052 10.611 0.000
GRAD 0.523 0.051 10.240 0.000
R-SQUARE
Observed Two-Tailed
Variable Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value
GRE 0.444 0.052 8.477 0.000
GRAD 0.477 0.051 9.333 0.000
QUALITY OF NUMERICAL RESULTS
Condition Number for the Information Matrix 0.348E-04
(ratio of smallest to largest eigenvalue)
MODEL RESULTS の下には、gre の hs と col への回帰のパス係数(スロープ)、そして grad の hs への回帰のパス係数が表示されています。標準化されていない係数(Estimateと書かれた列)と共に、標準誤差(S.E)、係数を標準誤差で割った値、そしてp値が示されている。ここから、hsとcolはgreを有意に予測し、greとhs(colは予測せず)はgradを有意に予測することがわかる。モデルからの追加パラメータは、パス係数の下に記載されている。これは、すべての係数(切片と傾き)が一緒に表示されるいくつかの汎用統計パッケージとは異なる。output: コマンドのstdyxオプションを使って標準化係数を要求したので、標準化結果も(非標準化結果の後に)出力に含まれます。STDYX標準化という見出しの下に、1単位の変化が元の変数の標準偏差の変化を表すように(標準化回帰モデルと同じように)標準化されたモデル・パラメータがすべてリストアップされている。標準化出力の一部として、R2乗の値がR-SQUAREの見出しの下に表示される。ここでは、我々のモデルの各従属変数の推定R2乗値が、標準誤差と仮説検定とともに与えられている。
2.間接効果および全体効果
パスモデルの魅力の1つは,間接効果だけでなく,全体効果(すなわち,変数間の関係)を評価することができる点である.全体効果とは、直接効果と間接効果の組み合わせであることに注意。この例では、hsのgradへの間接効果の推定を求めます(greを通して)。下図は、このモデルに対応する図であり、希望する間接効果は青色で示されている。入力ファイルに model indirect: コマンドを追加し、grad ind hs; を指定することで、間接効果の推定値を得ることができる。
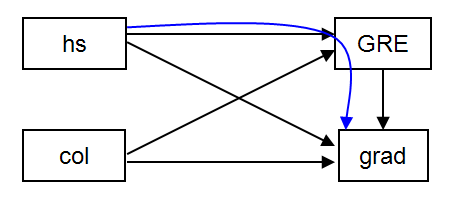
Title: Path analysis -- with indirect effects.
Data:
file is https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/path.dat ;
Variable:
Names are hs gre col grad;
Model:
gre on hs col;
grad on hs col gre;
Model indirect:
grad ind hs;
Output:
stdyx;
このモデルの出力は以下のとおりである。このモデルの出力は、全体効果、間接効果、直接効果を示すセクションが追加されている以外は、前のモデルと同じなので、出力の一部を省略している。間接効果の追加により、Mplusから追加の出力が要求されるが、モデル自体は変わらないので、出力は同じです。合計、間接、および直接効果の内訳は、合計、合計間接、特殊間接、および直接効果とラベル付けされたセクションで、モデル結果と標準化モデル結果の下に表示される。標準化された係数が要求されたため、標準化された総効果、間接効果、直接効果が標準化されていない効果の下に表示されている。
MODEL RESULTS
Two-Tailed
Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value
GRE ON
HS 0.309 0.065 4.756 0.000
COL 0.400 0.071 5.625 0.000
GRAD ON
HS 0.372 0.075 4.937 0.000
COL 0.123 0.084 1.465 0.143
GRE 0.369 0.078 4.754 0.000
Intercepts
GRE 15.534 2.995 5.186 0.000
GRAD 6.971 3.506 1.989 0.047
Residual Variances
GRE 49.694 4.969 10.000 0.000
GRAD 59.998 6.000 10.000 0.000
<output omitted>
QUALITY OF NUMERICAL RESULTS
Condition Number for the Information Matrix 0.348E-04
(ratio of smallest to largest eigenvalue)
TOTAL, TOTAL INDIRECT, SPECIFIC INDIRECT, AND DIRECT EFFECTS
Two-Tailed
Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value
Effects from HS to GRAD
Total 0.487 0.075 6.453 0.000
Total indirect 0.114 0.034 3.362 0.001
Specific indirect
GRAD
GRE
HS 0.114 0.034 3.362 0.001
Direct
GRAD
HS 0.372 0.075 4.937 0.000
STANDARDIZED TOTAL, TOTAL INDIRECT, SPECIFIC INDIRECT, AND DIRECT EFFECTS
STDYX Standardization
Two-Tailed
Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value
Effects from HS to GRAD
Total 0.465 0.068 6.858 0.000
Total indirect 0.109 0.032 3.455 0.001
Specific indirect
GRAD
GRE
HS 0.109 0.032 3.455 0.001
Direct
GRAD
HS 0.356 0.070 5.073 0.000
具体的な間接効果では、GRAD GRE HS と書かれた効果(それぞれが独立した行に表示され、最終結果が最初に表示されることに注意)は、GRE(上の青いパス)を通じて、新卒に対する HS の間接効果に対する推定係数を示している。直接効果と書かれた係数は、hsが学位に与える直接的な効果である。しかし、hsからgradへの有意な直接経路は、部分的な仲介に過ぎないことを示唆している。
3.具体的な間接効果
上記の例では、間接効果が1つしかないため、単純に過ぎた。多くの場合、モデルには複数の間接効果がある。この例では、hsからcolへの方向性パス(つまり回帰)を配置し、複数の間接効果の可能性があるモデルを作成する。下の図は、モデルを示しており、検討したい3つの間接パスを色付きの線で強調している。
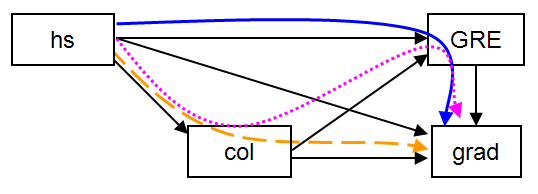
間接効果の計算を要求する方法はいくつかある。最初の方法は、前の例で示したもの(すなわち、grad ind hs;)で、hs から grad までのすべての間接パスを要求するものである。また、indを使って特定の間接パスを要求することもできます。例えば、以下ではgrad ind col hs;を使って、hs→col→gradの間接効果(つまり、上図のオレンジの破線のパス)を推定したいことを指定している。最後に、via を使って、第3の変数を通るすべての間接効果を要求できる。例えば、以下では、grad via gre hs; を使って、hs から grad へのすべての間接パスで gre を含むものを要求する。これは、hs から gre から grad(つまり、青の実線のパス)、hs から col から gre から grad(つまり、ピンクの点線のパス)である。新しい方向パス (col on hs;) と、モデル間接の特定の間接 (grad ind col hs;) と経由 (grad via gre hs;) オプションは、下図の入力で強調表示されている。
Title: Multiple indirect paths Data: file is https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/path.dat ; Variable: Names are hs gre col grad; Model: gre on col hs; grad on hs col gre; col on hs; Model indirect: grad ind col hs; grad via gre hs;
簡略化した出力は以下。このモデルの出力は、間接効果を示すセクションが追加されている以外は、以前のモデルの出力と同様の構造であることに注意。
<output omitted>
TOTAL, TOTAL INDIRECT, SPECIFIC INDIRECT, AND DIRECT EFFECTS
Two-Tailed
Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value
Effects from HS to GRAD
Sum of indirect 0.075 0.051 1.455 0.146
Specific indirect
GRAD
COL
HS 0.075 0.051 1.455 0.146
Effects from HS to GRAD via GRE
Sum of indirect 0.204 0.047 4.333 0.000
Specific indirect
GRAD
GRE
HS 0.114 0.034 3.362 0.001
GRAD
GRE
COL
HS 0.090 0.026 3.487 0.000
間接効果の最初のセット(HSからGRADへの効果)では、hs の col を通じた grad に対する間接効果が示されている。このモデルでは、hsのgradへの直接効果を推定したが、特定の間接効果を求めたため、この部分には表示されていない(上に表示されている)。間接効果の2番目のセット(HSからGREを経由したGRADへの効果)は、GREを含むhsからgradへのすべての間接効果(この場合、2つの間接効果がある)を示している。この出力は、hsがgradに対して全体として有意な間接効果(間接効果の和)を持ち、さらに2つの特定の間接効果(gre経由、colとgre経由)を持っていることを示している。この出力は、hsに対するgradの全効果を含んでいないことに注意。この出力では、前のモデルで行ったように、grad ind hsと指定するだけである。
過剰同定モデル
これは過剰同定モデルの例で、正の自由度を持つモデルである(飽和または単に同定されたと表現できる以前のモデルとは対照的である)。正の自由度を持つことで、CFIやRMSEAなどの適合指標とともに、モデル適合のカイ2乗検定を使用して、モデルの適合性を調査することができる。下の図では、モデルに含まれるパスは実線で表され、推定できるがそうでないパスは点線で表されている。hsはgradにもgreにも直接的な影響を与えず、colを経由してのみ影響を与えることに注意されたい。これは、高校の GPA は大学の GPA との関係を通してのみ、GRE の得点や大学院の成績と関連する、という仮説に対応するものである。
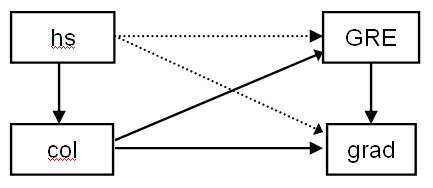
Title: Path analysis -- over identified model Data: file is https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/path.dat ; Variable: Names are hs gre col grad; Model: col on hs; gre on col; grad on col gre; Output: stdyx;
結果。
INPUT READING TERMINATED NORMALLY
Path analysis -- over identified model
SUMMARY OF ANALYSIS
Number of groups 1
Number of observations 200
Number of dependent variables 3
Number of independent variables 1
Number of continuous latent variables 0
Observed dependent variables
Continuous
GRE COL GRAD
Observed independent variables
HS
Estimator ML
Information matrix OBSERVED
Maximum number of iterations 1000
Convergence criterion 0.500D-04
Maximum number of steepest descent iterations 20
Input data file(s)
https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/path.dat
Input data format FREE
THE MODEL ESTIMATION TERMINATED NORMALLY
TESTS OF MODEL FIT
Chi-Square Test of Model Fit
Value 44.429
Degrees of Freedom 2
P-Value 0.0000
Chi-Square Test of Model Fit for the Baseline Model
Value 362.474
Degrees of Freedom 6
P-Value 0.0000
CFI/TLI
CFI 0.881
TLI 0.643
Loglikelihood
H0 Value -2811.629
H1 Value -2789.415
Information Criteria
Number of Free Parameters 10
Akaike (AIC) 5643.258
Bayesian (BIC) 5676.242
Sample-Size Adjusted BIC 5644.561
(n* = (n + 2) / 24)
RMSEA (Root Mean Square Error Of Approximation)
Estimate 0.3266
90 Percent C.I. 0.247 0.412
Probability RMSEA <= .05 0.000
SRMR (Standardized Root Mean Square Residual)
Value 0.086
MODEL RESULTS
Two-Tailed
Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value
COL ON
HS 0.605 0.048 12.500 0.000
GRE ON
COL 0.625 0.056 11.101 0.000
GRAD ON
COL 0.317 0.079 4.014 0.000
GRE 0.492 0.078 6.303 0.000
Intercepts
GRE 19.887 3.009 6.609 0.000
COL 21.038 2.576 8.165 0.000
GRAD 9.779 3.664 2.669 0.008
Residual Variances
GRE 55.313 5.531 10.000 0.000
COL 49.025 4.903 10.000 0.000
GRAD 67.311 6.731 10.000 0.000
STANDARDIZED MODEL RESULTS
STDYX Standardization
Two-Tailed
Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value
COL ON
HS 0.662 0.040 16.684 0.000
GRE ON
COL 0.617 0.044 14.112 0.000
GRAD ON
COL 0.276 0.068 4.092 0.000
GRE 0.434 0.065 6.671 0.000
Intercepts
GRE 2.103 0.397 5.298 0.000
COL 2.251 0.363 6.210 0.000
GRAD 0.913 0.375 2.436 0.015
Residual Variances
GRE 0.619 0.054 11.452 0.000
COL 0.561 0.053 10.677 0.000
GRAD 0.587 0.053 11.002 0.000
R-SQUARE
Observed Two-Tailed
Variable Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value
GRE 0.381 0.054 7.056 0.000
COL 0.439 0.053 8.342 0.000
GRAD 0.413 0.053 7.743 0.000
QUALITY OF NUMERICAL RESULTS
Condition Number for the Information Matrix 0.104E-03
(ratio of smallest to largest eigenvalue)
カイ二乗の値は、現在のモデルと飽和したモデルを比較する。我々のモデルは飽和していない(すなわち、我々のモデルは正の自由度を持つ)ので、カイ2乗値はもはやゼロではなく、モデルの適合性を評価するために使用することができる。同様に、同定されたばかりのモデルで1に等しかったCFIとTLIは、現在、情報量を持つ値になっている。さらに、RMSEAとSRMRは、情報量の多い値をとるようになりました(同定されたばかりのモデルでは、それらはゼロとして表示される)。正の自由度を持ち、したがって適合度指標に有益な値を持つことで、我々のモデルがどの程度データに適合しているかをよりよく評価することができる。このモデルからの具体的な係数推定値は、一般に、同定されたばかりのモデルと同じように解釈される。
R
データ読み込み
df1 <- read.table('https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/path.dat', sep=",")
colnames(df1)<-c("hs","gre","col","grad")
1.特定モデル

library(lavaan) model1 <- ' gre ~ hs gre ~ col grad ~ hs grad ~ col grad ~ gre ' fit1 <- sem(model = model1, data=df1) summary(fit1, standardized=TRUE)
結果。
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|) Std.lv Std.all
gre ~
hs 0.309 0.065 4.756 0.000 0.309 0.335
col 0.400 0.071 5.626 0.000 0.400 0.396
grad ~
hs 0.372 0.075 4.937 0.000 0.372 0.356
col 0.123 0.084 1.465 0.143 0.123 0.108
gre 0.369 0.078 4.755 0.000 0.369 0.326
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|) Std.lv Std.all
.gre 49.694 4.969 10.000 0.000 49.694 0.556
.grad 59.998 6.000 10.000 0.000 59.998 0.523
2.間接効果および全体効果

model2 <- ' # direct effect grad ~ c*hs # mediator gre ~ a*hs grad ~ b*gre # indirect effect (a*b) ab := a*b # total effect total := c + (a*b) # another path gre ~ col grad ~ col '
ラベルをそれぞれにつける。
独立変数Xにはc
従属変数Yにはb
媒介変数Mにはa
ラベルは任意でよい。間接効果の書き方は以下。
まず:=は母数を定義づけるための記号である。
abはa*bと定義づけられている。ここが間接効果に相当する。間接効果は構成する2つのパスの積であるため定義が積になっている。\
totalというのは総合効果であり、c + (a*b)と定義づけられる。ちなみにcは直接効果である。
fit2 <- sem(model = model2, data=df1) summary(fit2, standardized=TRUE)
3.具体的な間接効果

model3 <- ' # direct effect grad ~ c*hs # mediator gre ~ a*hs grad ~ b*gre gre ~ f*col col ~ d*hs grad ~ e*col # indirect effect ab := a*b # hs -> tre -> grad dfb := d*f*b # hs -> col -> gre -> grad de := d*e # hs -> col -> grad # total effect total_ind := (a*b) + (d*f*b) '
fit3 <- sem(model = model3, data=df1) summary(fit3, standardized=TRUE)
結果。
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|) Std.lv Std.all
grad ~
hs (c) 0.372 0.075 4.937 0.000 0.372 0.356
gre ~
hs (a) 0.309 0.065 4.756 0.000 0.309 0.335
grad ~
gre (b) 0.369 0.078 4.755 0.000 0.369 0.326
gre ~
col (f) 0.400 0.071 5.626 0.000 0.400 0.396
col ~
hs (d) 0.605 0.048 12.500 0.000 0.605 0.662
grad ~
col (e) 0.123 0.084 1.465 0.143 0.123 0.108
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|) Std.lv Std.all
.grad 59.998 6.000 10.000 0.000 59.998 0.523
.gre 49.694 4.969 10.000 0.000 49.694 0.556
.col 49.025 4.903 10.000 0.000 49.025 0.561
Defined Parameters:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|) Std.lv Std.all
ab 0.114 0.034 3.362 0.001 0.114 0.109
dfb 0.090 0.026 3.487 0.000 0.090 0.086
de 0.075 0.051 1.455 0.146 0.075 0.071
total_ind 0.204 0.047 4.332 0.000 0.204 0.195
hs -> tre -> grad: ab = 0.114
hs -> col -> gre -> grad : dfb = 0.090
hs -> col -> grad : de = 0.075
Effects from HS to GRAD via GRE
Sum of indirect : ab + dfb = 0.204
4.過剰同定モデル

model4 <- ' col ~ hs gre ~ col grad ~ col grad ~ gre ' fit4 <- sem(model = model4, data=df1) summary(fit4, standardized=TRUE, fit.measures=TRUE) #フィット指標の表示
結果。
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 7
Number of observations 200
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 44.429
Degrees of freedom 2
P-value (Chi-square) 0.000
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 362.474
Degrees of freedom 6
P-value 0.000
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 0.881
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 0.643
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -2062.830
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -2040.616
Akaike (AIC) 4139.660
Bayesian (BIC) 4162.748
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (BIC) 4140.571
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.326
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.247
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.412
P-value RMSEA <= 0.05 0.000
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.102
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|) Std.lv Std.all
col ~
hs 0.605 0.048 12.500 0.000 0.605 0.662
gre ~
col 0.625 0.056 11.101 0.000 0.625 0.617
grad ~
col 0.317 0.079 4.014 0.000 0.317 0.276
gre 0.492 0.078 6.303 0.000 0.492 0.434
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|) Std.lv Std.all
.col 49.025 4.903 10.000 0.000 49.025 0.561
.gre 55.313 5.531 10.000 0.000 55.313 0.619
.grad 67.311 6.731 10.000 0.000 67.311 0.587